Introduction to PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
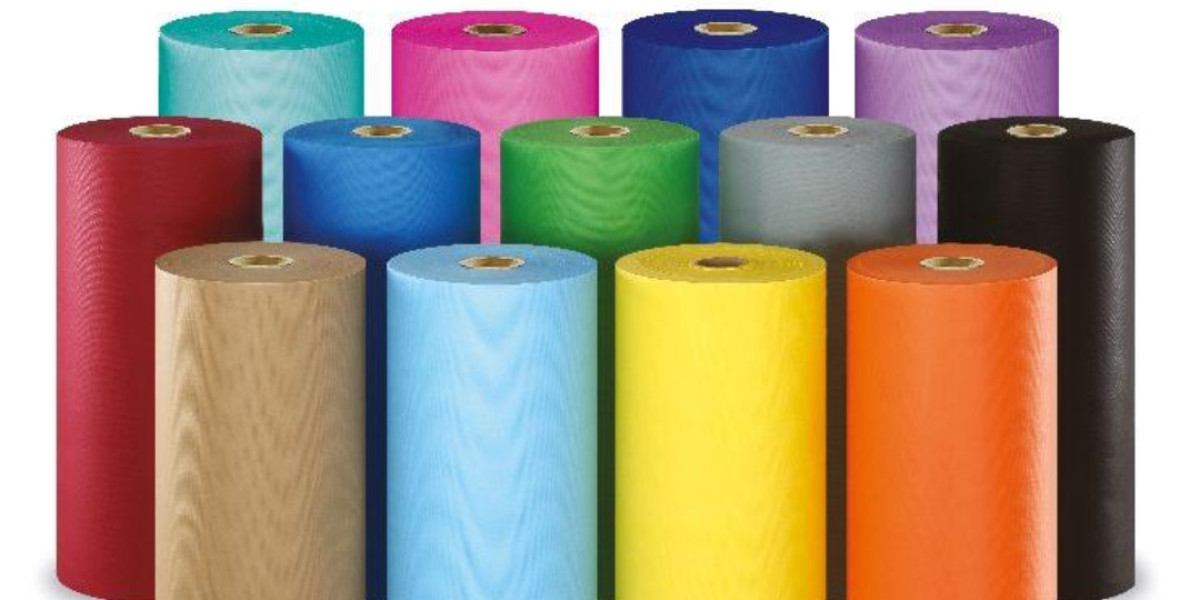
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric, composed primarily of polypropylene (PP), has become increasingly popular in a variety of industries due to its unique properties and wide range of applications. This fabric is produced through a process that involves spinning filaments of polypropylene and bonding them together without the need for weaving or knitting. The resulting nonwoven fabric is highly durable, lightweight, and resistant to many environmental factors, making it particularly useful for both industrial and consumer applications. Over the years, the manufacturing techniques for Pulkit Plastic Products have evolved, allowing for the production of various grades and specifications to meet the diverse needs of modern markets.
Characteristics and Benefits
One of the standout features of nonwoven spunbond fabric is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. The fabric is lightweight, yet it possesses considerable tensile strength, which is crucial in applications requiring durability and robust performance. Furthermore, the fabric is resistant to tearing, making it suitable for various demanding environments. Another key benefit is its permeability; spunbond nonwoven fabric exhibits good air, liquid, and moisture vapor permeability, which allows for breathability without compromising protection.
Additionally, PP spunbond fabric is naturally chemical-resistant, contributing to its versatility in applications ranging from medical supplies to agricultural covers. Its resistance to UV light is another significant advantage, ensuring enhanced longevity when used in outdoor settings. Furthermore, nonwoven spunbond fabric can be manufactured in a variety of colors and thicknesses, offering customization options that cater to specific industry requirements and aesthetic preferences.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of Spunbond nonwoven fabric involves several key stages. First, polypropylene granules are melted and extruded into continuous filaments through spinnerets, similar to the method used to produce traditional textiles. The filaments are then rapidly cooled and laid out onto a conveyor, where they are bonded together using heat and pressure. This method, known as thermal bonding, provides a uniform and consistent fabric structure without the need for additional processing agents or chemicals.
After the bonding process, the fabric can be treated further based on its intended application. Additional treatments may include hydrophilization, antimicrobial finishing, or dyeing to meet specific performance standards. This capability to modify the fabric according to particular needs ensures that PP spunbond nonwoven fabric remains adaptable across multiple industries. The result is a high-quality, versatile fabric that fulfills a myriad of functional and aesthetic purposes.
Applications Across Industries
The applications of spunbond nonwoven fabric are extensive, reflecting its versatility and outstanding characteristics. One of the most prominent uses of this fabric is in the disposable hygiene products market. PP spunbond fabric is widely utilized in the production of diapers, feminine hygiene products, and adult incontinence supplies, where its softness, absorbency, and skin-friendly properties align with user needs.
In the medical field, nonwoven spunbond fabric is commonly found in surgical gowns, masks, and drapes, where sterility and protection from contaminants are paramount. The fabric’s ability to resist fluids, combined with its breathability, ensures both comfort and safety for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Additionally, the agricultural sector leverages the properties of spunbond nonwoven fabric for crop covers, weed control fabrics, and horticultural textiles, offering protection and enhancing growing conditions for plants.
The construction industry also benefits from using PP spunbond nonwoven fabric. It is employed as a geotextile for soil erosion control, landscaping, and drainage applications due to its excellent filtration and separation properties. Furthermore, the fabric is used in insulation materials and as a moisture barrier in building projects, where durability and resistance to environmental factors are essential.
Environmental Considerations
With growing awareness around environmental sustainability, the production and use of nonwoven fabrics, including PP spunbond, are also being scrutinized. Traditional plastic materials have faced criticism for their contribution to pollution and waste management challenges. However, there are significant strides being made in the development of sustainable alternatives.
Many manufacturers are now focusing on creating eco-friendly spunbond nonwoven fabric options using recycled polypropylene or bio-based materials. Additionally, the lightweight nature of spunbond fabric reduces the amount of raw material needed for production, which in turn can lead to lower energy consumption during manufacturing. Furthermore, the recyclability of nonwoven materials is gaining traction, allowing them to be repurposed into new products and reducing overall environmental impact.
By prioritizing sustainability in both the production process and product life cycle, manufacturers can meet consumer demand for environmentally-friendly products while maintaining performance and application benefits. As global attention towards eco-conscious choices continues, the evolution of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric reflects a broader commitment to responsible manufacturing practices.
Market Trends and Innovations
The Non woven spunbond industry is continuously evolving, driven by innovations in technology and changing market dynamics. One notable trend involves the integration of smart textiles into spunbond nonwoven fabric. Manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate properties such as moisture-wicking, odor control, and even antimicrobial features directly into the fibers, enhancing the functionality of the fabric for various applications.
Another exciting development is the use of digital printing technologies on PP spunbond fabric, allowing for high-definition graphics and intricate designs. This innovation is particularly useful for promotional and branding uses, enabling businesses to create visually appealing products that stand out in the market. The capacity for customization is increasingly becoming a differentiating factor, especially as brands look to personalize their offerings.
Developments in automation and manufacturing processes are also driving efficiencies, reducing production times, and minimizing waste. As companies invest in advanced machinery and techniques, the cost-effectiveness of producing spunbond nonwoven fabric can improve, allowing for lower pricing to enhance competitiveness.
Challenges in the Industry
While the prospects for PP spunbond nonwoven fabric are promising, the industry does face challenges that need to be addressed. One of the primary issues is the regulatory landscape regarding environmental compliance. As regulations surrounding plastic production and waste management become stricter, manufacturers must adapt to meet these standards while maintaining product quality and cost efficiency.
Another significant challenge centers around competition from alternative materials. With the emergence of biodegradable nonwoven fabrics and natural fibers, spunbond nonwoven manufacturers must demonstrate the unique advantages of their products. This may necessitate increased investment in research and development to improve performance characteristics or reduce environmental footprints.
Supply chain disruptions, particularly in light of global events such as pandemics or geopolitical issues, also pose challenges to the industry. Ensuring a stable supply of raw materials at competitive prices while navigating shipping and logistical hurdles remains a constant consideration for manufacturers.
Conclusion
The Spun bonded non woven fabric has emerged as a versatile, durable, and essential material in a wide range of applications, reflecting its significance across industries such as healthcare, agriculture, construction, and consumer goods. Its unique properties and adaptability enable it to meet diverse functional and aesthetic needs, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers. As the market evolves, so too do the opportunities for innovation and sustainability within the industry. By continuing to develop eco-friendly practices and responding to consumer demands, the future of spunbond nonwoven fabric looks bright and promising.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is spunbond nonwoven fabric, and how is it made?
Spunbond nonwoven fabric is a type of fabric made from polypropylene that is produced by extruding filament fibers that are then bonded together without weaving or knitting. The manufacturing process involves spinning, cooling, and bonding the fibers using heat and pressure to form a durable nonwoven material.
2. What are the main applications of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is commonly utilized in disposable hygiene products, medical supplies, agricultural applications, and construction materials. Its versatility makes it suitable for a range of products including diapers, surgical gowns, crop covers, and geotextiles.
3. Is spunbond nonwoven fabric eco-friendly?
While traditional spunbond nonwoven fabric is made from polypropylene, efforts are underway to develop more sustainable alternatives using recycled materials or bio-based options. Additionally, many spunbond fabrics can be recycled after use, contributing to reduced environmental impact.
4. How do manufacturers ensure quality in spunbond nonwoven fabric production?
Manufacturers often implement strict quality control measures throughout the production process, which include testing for tensile strength, thickness, and permeability. Advanced manufacturing technologies and adherence to industry standards also contribute to ensuring the quality and consistency of spunbond nonwoven fabric.