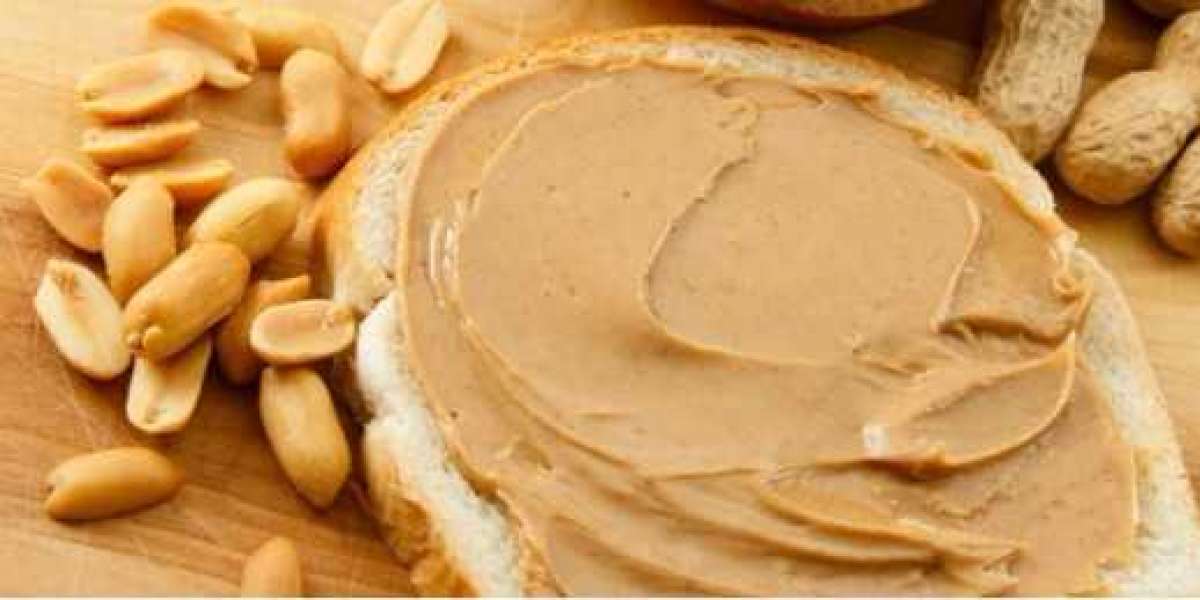
Peanut butter is a pantry staple, beloved by millions around the world. Whether spread on toast, mixed into smoothies, or simply eaten straight from the jar, its creamy texture and rich flavor have a unique way of captivating our taste buds. But what makes peanut butter so addictive? Is it the combination of fats, sugars, and salt, or is there something more complex at play? In this analysis, we'll explore the factors behind peanut butter's irresistible appeal, including its chemical makeup, sensory experience, and psychological triggers. We'll also briefly touch on how food companies like Nutrionex Foods have responded to consumer demand for this beloved spread.
1. The Perfect Balance of Fat, Sugar, and Salt
One of the primary reasons peanut butter is so addictive lies in its composition of fat, sugar, and salt—a combination often referred to as the "bliss point" in food science. The bliss point refers to the exact ratio of these three ingredients that make a food highly palatable and difficult to resist.
Fats: Peanut butter contains a significant amount of fat, approximately 50% of its weight. Most of this fat is unsaturated, which is healthier than saturated fat, but fat in general plays a vital role in the addictive nature of food. Fat is energy-dense, meaning that it provides a lot of calories in a small amount, and our bodies have evolved to crave energy-dense foods. Additionally, fats enhance the texture of foods, making peanut butter creamy and smooth.
Sugar: While natural peanut butter contains only the sugars found in peanuts, many commercial brands add sugar to enhance the flavor. Sugar triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This makes us want to eat more, and as we consume sugar regularly, we begin to crave it even more.
Salt: Salt is another crucial component. It doesn't just enhance the flavor of peanut butter but also helps to balance out the richness of the fat and the sweetness of the sugar. Salt, like sugar, can also stimulate dopamine release, adding to the addictive cycle.
The perfect balance of these ingredients creates a sensory experience that is difficult to resist. Companies like Nutrionex Foods capitalize on this by developing formulations of peanut butter that cater to consumer tastes, making their products more appealing and, ultimately, more addictive.
2. The Role of Texture in Food Addiction
The texture of peanut butter is another critical factor that adds to its addictive properties. Whether smooth or crunchy, the sensation of peanut butter in the mouth is deeply satisfying.
Creaminess: The smoothness of peanut butter coats the mouth in a way that feels indulgent and comforting. The creamy texture is often associated with richness, making the food seem more luxurious and enjoyable. This sensation triggers positive feelings in the brain, which reinforces the desire to eat more.
Crunchiness: On the other hand, peanut butter with crunchy pieces appeals to people who enjoy a combination of textures. Crunchy foods are known to increase feelings of satisfaction and fullness, possibly because they require more chewing. The combination of smooth and crunchy elements makes the eating experience even more enjoyable and varied, increasing the likelihood of overconsumption.
The combination of texture and flavor creates a multi-sensory experience that the brain finds particularly rewarding. As we eat peanut butter, the sensory feedback we receive from its texture and taste strengthens our cravings.
3. Peanut Butter and Dopamine: The Brain's Reward System
Peanut butter doesn't just taste good—it also stimulates the brain's reward centers in a way that encourages repeated consumption. When we eat peanut butter, especially varieties with added sugar and salt, our brains release dopamine. This is the same chemical that's involved in other pleasurable activities, such as exercise, listening to music, and even drug use.
Dopamine is the brain's "feel-good" neurotransmitter, and its release creates a sensation of pleasure and reward. This reward mechanism evolved to help us survive by encouraging behaviors that are beneficial, like eating high-energy foods. However, in modern society, where food is readily available, this system can work against us. Highly palatable foods like peanut butter can lead to a cycle of craving and overconsumption as our brains seek out the dopamine "high" they provide.
Interestingly, peanut butter's high fat content also plays a role in this cycle. Fatty foods are particularly effective at triggering dopamine release because they are energy-dense and historically valuable for survival. As a result, the brain is wired to find foods rich in fats extremely rewarding, making peanut butter a prime candidate for overindulgence.
4. Emotional and Psychological Factors
Beyond its chemical and sensory properties, peanut butter can also have emotional and psychological connections that contribute to its addictive nature. For many people, peanut butter is a comfort food, often associated with childhood memories, family, and home.
Nostalgia and Comfort: Peanut butter is often one of the first foods introduced to children. It's versatile, easy to prepare, and often included in simple, nostalgic meals like peanut butter and jelly sandwiches. As a result, peanut butter can evoke feelings of comfort and security, making it a go-to food during stressful times.
Stress Eating: Emotional eating is a common phenomenon, and peanut butter, with its high fat and sugar content, is a prime target. During periods of stress or emotional turmoil, many people turn to comforting, high-calorie foods for a temporary sense of relief. This behavior can reinforce a cycle of using peanut butter as a coping mechanism, leading to frequent cravings.
5. Marketing and Availability: How Companies Keep Us Hooked
In addition to its sensory and psychological appeal, the way peanut butter is marketed and sold can also contribute to its addictive qualities. Food companies are keenly aware of the factors that make peanut butter so popular, and they design their products accordingly.
NutriOnex Foods, for example, uses strategic branding and product development to cater to health-conscious consumers while still providing the indulgent experience people expect from peanut butter. They offer varieties that are labeled as natural or low-sugar, yet these products still contain the fats and salts that make peanut butter so hard to resist.
Packaging and Marketing: Peanut butter is often marketed as a versatile, protein-rich food that can be part of a healthy diet. However, its addictive qualities make it easy to overconsume. The convenience of peanut butter—available in single-serving packs, snack bars, and spreads—makes it easy to incorporate into any meal or snack, increasing its consumption.
Furthermore, peanut butter's accessibility and relatively low cost make it a staple in many households, further fueling its consumption. The ubiquity of peanut butter in stores and its prominent placement on grocery shelves reinforces its status as a household essential, ensuring that it's always within reach.
Conclusion
Peanut butter's addictive nature is the result of a complex combination of factors. Its perfect balance of fat, sugar, and salt creates a highly palatable food that appeals to our taste buds and stimulates our brain's reward centers. The texture of peanut butter, whether smooth or crunchy, adds to its sensory appeal, while its association with comfort and nostalgia gives it emotional significance. Food companies like Nutrionex Foods are well aware of these factors and continue to produce peanut butter products that cater to consumers' tastes and desires.
Ultimately, peanut butter is addictive because it triggers pleasure in both the body and mind. Its combination of fats, sugars, and salt provides immediate sensory satisfaction, while its emotional and psychological connections keep us coming back for more. While peanut butter can be part of a balanced diet, it's essential to be mindful of portion sizes and consumption habits to avoid overindulgence.